Boostcamp AI Tech (P3 - Day02)
Peer session
- 토론, 의견 나눔
- 어제 과제
- 베이스라인 코드
- (현우님) 자동으로 output 파일을 리더보드에 제출하는 submit.py 파일 구현 후 공유 (description 값도 지정 가능한 version)
- Git
- 팀 repository에 각자 branch 생성
- 팀 repository에 각자 branch 생성
오피스 아워
- My Question
- unknown 클래스가 “기타 등등”의 의미라면, 학습에서 unknown 클래스를 제외하고 inference 시 11개 클래스 중 confident하게 예측되는 것이 없을 경우에 unknown으로 예측하는 방법도 의미 있는 시도가 될까요?
- 답변: 재미있는 생각인데, unknown 클래스의 유형과 분포가 굉장히 다양하고 종잡을 수 없다면 의미 있는 시도가 될 것 같다. 엄밀한 EDA를 통해 데이터 분포를 파악한 뒤 고려해볼 것을 추천한다.
- 답변: 재미있는 생각인데, unknown 클래스의 유형과 분포가 굉장히 다양하고 종잡을 수 없다면 의미 있는 시도가 될 것 같다. 엄밀한 EDA를 통해 데이터 분포를 파악한 뒤 고려해볼 것을 추천한다.
- unknown 클래스가 “기타 등등”의 의미라면, 학습에서 unknown 클래스를 제외하고 inference 시 11개 클래스 중 confident하게 예측되는 것이 없을 경우에 unknown으로 예측하는 방법도 의미 있는 시도가 될까요?
프로젝트 활동
- mIoU score: 0.3170 달성
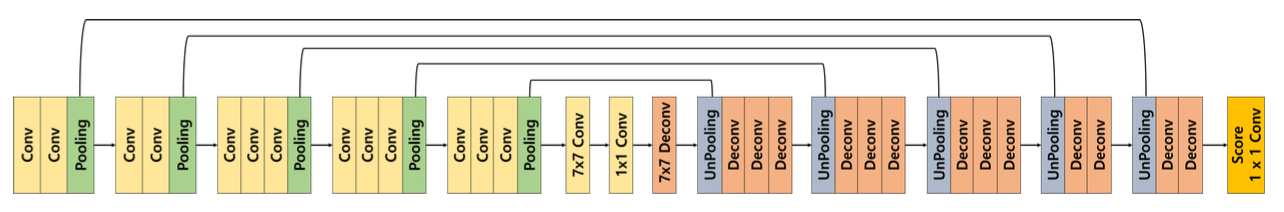
- Model: DeconvNet
- 바꾼 hyperparam
- Resize(256, 256)
- epoch=10
-
DeconvNet 모델 구현하기
class DeconvNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_classes=21): super(DeconvNet, self).__init__() self.pretrained_model = vgg16(pretrained = True) features, classifiers = list(self.pretrained_model.features.children()), list(self.pretrained_model.classifier.children()) self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(*features[:4]) self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2, ceil_mode=True, return_indices=True) self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(*features[5:9]) self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2, ceil_mode=True, return_indices=True) self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(*features[10:16]) self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2, ceil_mode=True, return_indices=True) self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(*features[17:23]) self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2, ceil_mode=True, return_indices=True) self.conv5 = nn.Sequential(*features[24:30]) self.pool5 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2, ceil_mode=True, return_indices=True) self.fc6 = CBR(512, 4096, 7, 1, 0) self.drop6 = nn.Dropout2d(0.5) self.fc7 = CBR(4096, 4096, 1, 1, 0) self.drop7 = nn.Dropout2d(0.5) self.fc6_deconv = DCB(4096, 512, 7, 1, 0) self.unpool5 = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2) self.deconv5_1 = DCB(512, 512) self.deconv5_2 = DCB(512, 512) self.deconv5_3 = DCB(512, 512) self.unpool4 = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2) self.deconv4_1 = DCB(512, 512) self.deconv4_2 = DCB(512, 512) self.deconv4_3 = DCB(512, 256) self.unpool3 = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2) self.deconv3_1 = DCB(256, 256) self.deconv3_2 = DCB(256, 256) self.deconv3_3 = DCB(256, 128) self.unpool2 = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2) self.deconv2_1 = DCB(128, 128) self.deconv2_2 = DCB(128, 64) self.unpool1 = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2) self.deconv1_1 = DCB(64, 64) self.deconv1_2 = DCB(64, 64) self.score_fr = nn.Conv2d(64, num_classes, 1, 1, 0, 1) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x, pool1_indices = self.pool1(x) x = self.conv2(x) x, pool2_indices = self.pool2(x) x = self.conv3(x) x, pool3_indices = self.pool3(x) x = self.conv4(x) x, pool4_indices = self.pool4(x) x = self.conv5(x) x, pool5_indices = self.pool5(x) x = self.drop6(self.fc6(x)) x = self.drop7(self.fc7(x)) x = self.fc6_deconv(x) x = self.unpool5(x, pool5_indices) x = self.deconv5_1(x) x = self.deconv5_2(x) x = self.deconv5_3(x) x = self.unpool4(x, pool4_indices) x = self.deconv4_1(x) x = self.deconv4_2(x) x = self.deconv4_3(x) x = self.unpool3(x, pool3_indices) x = self.deconv3_1(x) x = self.deconv3_2(x) x = self.deconv3_3(x) x = self.unpool2(x, pool2_indices) x = self.deconv2_1(x) x = self.deconv2_2(x) x = self.unpool1(x, pool1_indices) x = self.deconv1_1(x) x = self.deconv1_2(x) x = self.score_fr(x) return x def CBR(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1): return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU()) def DCB(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1): return nn.Sequential(nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU())
강의
-
FCN의 한계점
- 객체의 크기가 크거나 작은 경우 예측 잘 못함
- 큰 객체의 경우 지역적 정보만으로 예측
- 같은 객체도 다르게 labeling
- 작은 객체 무시되는 경우 발생
- 객체의 디테일한 모습이 사라지는 문제 (경계 학습 어려움)
- 객체의 크기가 크거나 작은 경우 예측 잘 못함
-
Decoder를 개선한 models
- DeconvNet
- Decoder를 Encoder와 대칭으로 만든 형태
- Unpooling
- MaxPool 시 max 값의 인덱스 정보를 저장 후 unpool 시 복원
- max index가 아닌 부분이 0으로 채워져 sparse activation map을 가지기 때문에, transposed convolution을 수행해 채워줌
- example-specific (자세한) 구조를 잡아냄
- Deconvolution
- (=transposed convolution)
- input object의 모양 복원
- unpooled된 구조에 빈 부분을 채워 넣어 class-specific한 구조를 잡아냄
- 얕은 층의 경우 전반적 모습을, 깊은 층의 경우 구체적인 모습을 잡아냄
- SegNet
- Road scene understanding application 분야에서 (real-time) semantic segmentation 수행
- DeconvNet과 비슷하지만, 중간에 7x7conv 1x1conv 7x7deconv 레이어가 없고, decoder 부분에 deconv 대신 conv가 쓰임
- weight parameter 수가 감소해 학습 및 추론 시간이 빠름
- DeconvNet
-
Skip connection을 적용한 models
- FC DenseNet
- Unet
-
Receptive field를 확장시킨 models
- DeepLab v1
- Dilated convolution
- conv와 conv 사이 max pooling을 넣으면 receptive field를 넓힐 수 있지만, 다시 이미지 원본 사이즈로 upsample 시 resolution이 낮아짐 (low feature resolution)
- filter size를 키워도 receptive field를 넓힐 수 있지만, 파라미터 수가 폭증함
- dilated convolution (atrous convolution)을 이용하면 이 문제들을 겪지 않으면서 receptive field 넓힐 수 있음
- 그림
- Bilinear interpolation
- upsample 시 0으로 채우는 것이 아니라, 근처 값들과 가까울 수록 그 값과 비슷하게 채움 (내분)
- $(7, \square, \square, 9)$
- $\frac{4}{2+4} \times 7 + \frac{2}{2+4} \times 9 = 7.66$
- $\frac{2}{2+4} \times 7 + \frac{4}{2+4} \times 9 = 8.33$
- $(7, 7.66, 8.33, 9)$
- Dilated convolution
- DilatedNet
- Front + Basic context module(다양한 conv rate를 준 conv layer들의 block)
- DeepLab v2
- Multi-scale image (다양한 conv rate를 준 conv layer들을 병렬로 배치)
- ASPP (Parallel moduels with atrous convolution)
- Multi-scale image (다양한 conv rate를 준 conv layer들을 병렬로 배치)
- PSPNet
- 도입 배경 (문제점들)
- mismatched relationship
- confusion categories
- inconspicous(불명확한) classes
- Global average pooling
- 주변 정보 (문맥)을 파악해 객체 예측에 사용
- 여러 개를 병렬로 묶어 pyramid pooling module 사용
- 도입 배경 (문제점들)
- DeepLab v3
- ASPP, augmented with image-level features (DeepLab v2 + global average pooling)
- ASPP, augmented with image-level features (DeepLab v2 + global average pooling)
- DeepLab v1